Control System Synthesis¶
- control.lqr(*args, **keywords)¶
Linear quadratic regulator design
The lqr() function computes the optimal state feedback controller that minimizes the quadratic cost
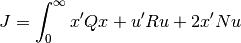
The function can be called with either 3, 4, or 5 arguments:
- lqr(sys, Q, R)
- lqr(sys, Q, R, N)
- lqr(A, B, Q, R)
- lqr(A, B, Q, R, N)
Parameters: A, B: 2-d array
Dynamics and input matrices
sys: Lti (StateSpace or TransferFunction)
Linear I/O system
Q, R: 2-d array
State and input weight matrices
N: 2-d array, optional
Cross weight matrix
Returns: K: 2-d array
State feedback gains
S: 2-d array
Solution to Riccati equation
E: 1-d array
Eigenvalues of the closed loop system
Examples
>>> K, S, E = lqr(sys, Q, R, [N]) >>> K, S, E = lqr(A, B, Q, R, [N])
- control.place(A, B, p)¶
Place closed loop eigenvalues
Parameters: A : 2-d array
Dynamics matrix
B : 2-d array
Input matrix
p : 1-d list
Desired eigenvalue locations
Returns: K : 2-d array
Gains such that A - B K has given eigenvalues
Examples
>>> A = [[-1, -1], [0, 1]] >>> B = [[0], [1]] >>> K = place(A, B, [-2, -5])